LesionDiff: Synthetic Data via Lesion Information Transfer Diffusion Model Facilitates Plant Disease Diagnosis. Accurate plant disease identification is crucial for effective control and yield improvement, but deep learning models often require large datasets, which are limited by environmental variability and growth stages. To address this, we propose LesionDiff, a lesion-guided image generation framework that enhances data diversity and realism. It integrates lesion detection (GroundingDINO), lesion-focused augmentation, and a CLIP-guided cross-attention U-Net to synthesize disease regions. Experiments show that LesionDiff improves diagnostic accuracy by over 3% on real-world datasets, demonstrating its effectiveness in boosting plant disease recognition.
overview: We propose LesionDiff, as shown in Fig.1, a lesion-driven image generation framework that synthesizes realistic plant disease images aligned with human perception. It combines lesion detection via fine-tuned GroundingDINO, lesion-centered data enhancement, and CLIP-guided image reconstruction using a cross-attention U-Net. By transferring key lesion information through a diffusion process, LesionDiff effectively enriches disease data and enhances plant disease diagnosis.
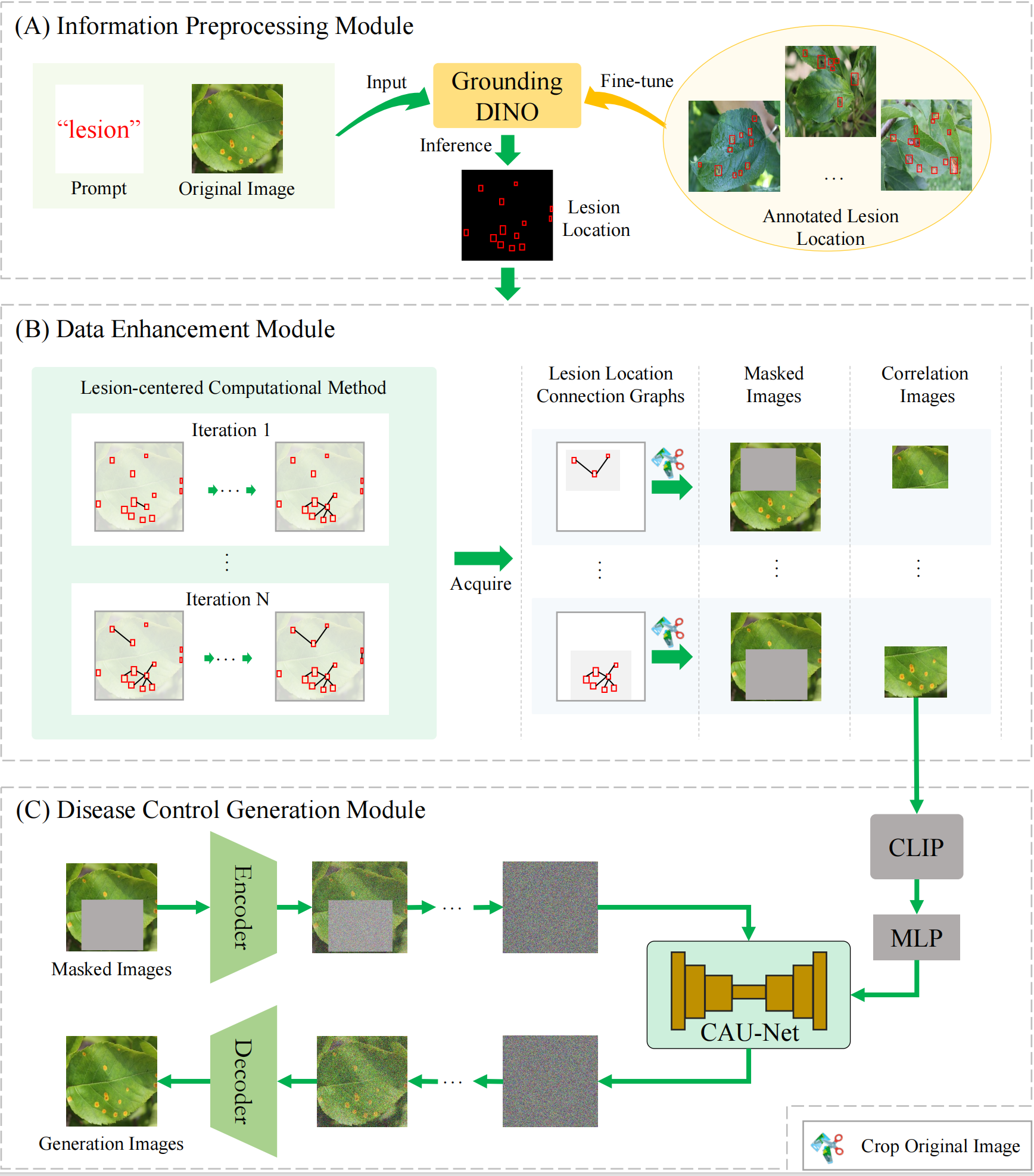
Figure 1: The LesionDiff framework. (A) The information preprocessing module. (B) The disease data enhancement module. (C) The disease control generation module.
Information Preprocessing Module In LesionDiff, correlation images guide the generation of masked disease regions. As shown in Fig.1(A), we fine-tune GroundingDINO on annotated lesion data using the prompt "lesion" to accurately extract lesion locations from original plant disease images. These precise lesion maps enable the creation of high-quality correlation images, providing a reliable foundation for subsequent data enhancement and image synthesis.
Disease Data Enhancement Module As shown in Fig.1(B), to address the complexity and variability of plant disease distributions in natural environments, we adopt a lesion-centered masking strategy inspired by MAE. This approach constructs lesion location connection graphs by aggregating lesions with similar spatial patterns, providing more structured location information. These graphs guide the creation of masked and correlated images, enhancing the model’s ability to learn disease phenotypes and generate accurate plant disease images.
Disease Control Generation Module As shown in Fig.1(C), traditional GAN-based methods in smart agriculture often struggle to generate plant disease images with sufficient diversity and realism. To address this, we propose a disease control generation module that combines a denoising diffusion probabilistic model (DDPM) with the CLIP model. The framework encodes visual features from both masked and original images, fuses them, and feeds them into a diffusion model for generation. To enhance image fidelity and diversity, CLIP-derived features from correlation images are used to guide the process, with a cross-attention U-Net (CAU-Net) facilitating feature fusion, as further illustrated in Fig.2.
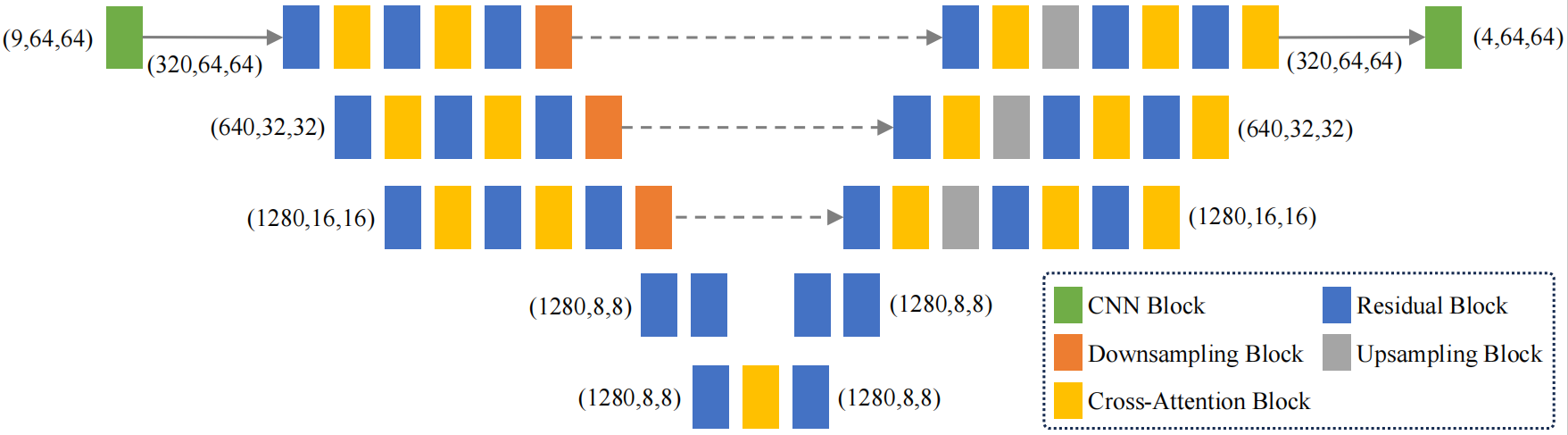
Figure 2: The CAU-Net in the disease control generation module.
